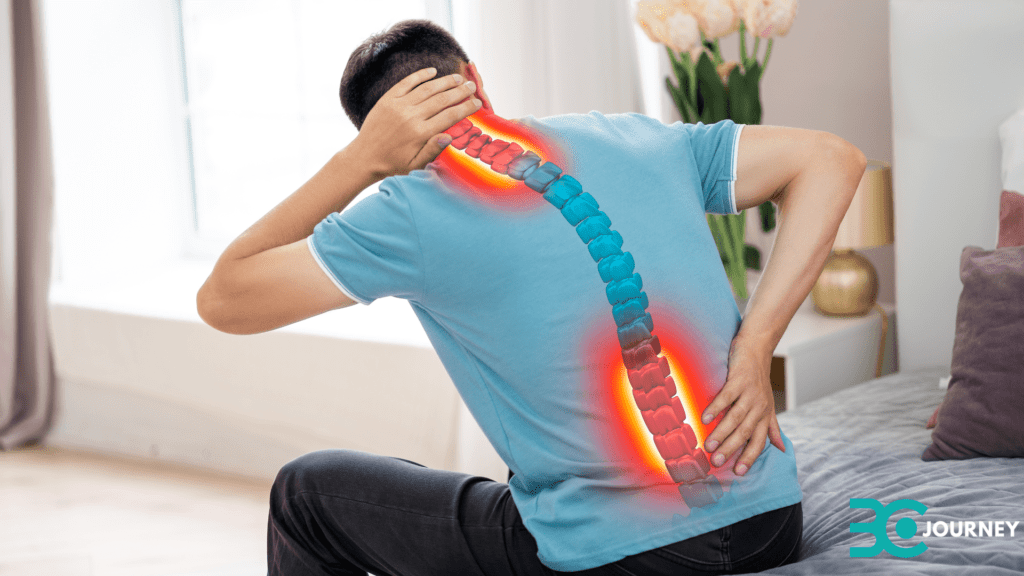
Back pain
Back pain is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to any discomfort, stiffness, or pain experienced in the back area, specifically in the upper back, middle back, and lower back. It can range from mild and occasional discomfort to severe and chronic pain that interferes with daily activities.
Various factors contribute to back pain, such as age, lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and injuries. Our muscles lose strength and flexibility as we age, making them more prone to strain and injury. Poor posture, a lack of physical activity, and being overweight also increase the risk of developing back pain.
Certain medical conditions, like arthritis, osteoporosis, and spinal stenosis, can also cause back pain. Injuries from accidents or sports activities can damage the muscles, ligaments, or discs in the back, leading to pain.
Back pain can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and productivity. It can limit their ability to perform daily tasks and even lead to disability in severe cases.
In this Markdown document, we will discuss some common causes of back pain and practical tips for managing and preventing it.
THE ANATOMY OF THE BACK
Before we dive into the causes of back pain, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of the back. The back is a complex structure consisting of bones, muscles, ligaments, and discs that support the body and allow us to move.
Thirty-three vertebrae, stacked on each other, make up the spine, also known as the backbone. These vertebrae are divided into five regions:
1.Cervical (neck)
2.Thoracic (upper back)
3.Lumbar (lower back)
4.Sacrum (pelvis)
5.Coccyx (tailbone)
Small cushions called intervertebral discs between each vertebra act as shock absorbers.
The muscles in our back support our posture and help us move in different directions. The ligaments connect the bones and provide stability to the spine.
Keeping our backs strong and flexible is crucial for preventing and managing back pain. Now, let’s look at some common factors contributing to back pain.
What are the factors associated with back pain?
As mentioned earlier, various factors can lead to back pain. Let’s examine some of them.
Age: Our muscles lose strength and flexibility as we age, making them more prone to strain and injury.
Lifestyle habits: Poor posture, a lack of physical activity, and being overweight can strain the back muscles.
Medical conditions: Certain conditions, like arthritis, osteoporosis, and spinal stenosis, can cause back pain.
Injuries: Accidents or sports activities can damage the muscles, ligaments, or discs in the back, leading to pain.
Infections: In rare cases, back pain can be caused by infections in the spine, such as osteomyelitis or discitis.
Poor Posture: Sitting or standing in an incorrect posture for extended periods can strain the muscles and lead to back pain.
Osteoporosis: This condition causes the bones to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures and back pain.
Stress: Emotional stress can cause muscle tension in the back, leading to discomfort and pain.
Who is most likely to experience back pain?

Back pain can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. However, certain factors may increase a person’s risk of developing back pain.
People who are overweight: people who take high-calorie and fat diets are more prone to back pain because it puts extra strain on the muscles and bones.
People with poor posture: Sitting or standing in an incorrect posture for extended periods can create muscle imbalances and strain the back muscles.
Pregnant women: The weight gain and hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause back pain, especially in the lower back.
Individuals with physically demanding jobs: Jobs that require heavy lifting or repetitive movements can strain the back muscles, leading to pain.
Smokers: Smoking can restrict blood flow to the spine, which may lead to the degeneration of spinal discs and increase the risk of back pain.
Heredity: Genetics also influences the risk of developing back pain. Certain conditions, like scoliosis (an abnormal spine curvature), can be inherited and may cause back pain.
Age: Our bones and muscles weaken, increasing the risk of back pain.
The following sections will discuss practical tips for managing and preventing back pain. By making simple lifestyle changes and taking care of your back, you can reduce the chances of experiencing back pain and improve your overall health and well-being.
How do I avoid back pain? Practical Tips for Managing Back Pain
If you are currently experiencing back pain or want to prevent it in the future, here are some practical tips that can help.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight strains the back muscles and can increase the risk of developing back pain.
Practice Good Posture: Maintain correct posture while sitting, standing, and lifting heavy objects. Avoid slouching or hunching over your desk, as this can strain your back muscles unnecessarily.
Stay Active: Regular exercise helps keep your back muscles strong and flexible. Choose low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga that are gentle on the back.
Use Proper Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, always bend at the knees and use the leg muscles instead of your back. Also, avoid twisting while lifting.
Take Breaks from Sitting: If you have a sedentary job, take breaks and move around every 30 minutes. Sitting for extended periods can strain the back muscles.
Use supportive furniture. Invest in an ergonomic chair that supports your back while sitting at a desk. Sleep on a supportive mattress and pillows to ensure proper spine alignment.
Manage Stress: Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce muscle tension in the back.
Quit Smoking: As mentioned earlier, smoking can increase the risk of back pain by restricting blood flow to the spine. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the chances of developing back pain.
When should I go to the hospital for back pain?
What are the treatments and diagnoses for back pain?
If you are experiencing persistent or severe back pain, it is essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The most common methods used for diagnosing back pain include:
Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your spine and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to identify any structural abnormalities in the spine.
Bone Scans: This test can help identify bone abnormalities or infections in the spine.
Blood Test: In rare cases, a blood test may be done to check for underlying medical conditions that could be causing back pain.
Electromyogram (EMG): This test measures electrical activity in the muscles and nerves to determine if there is nerve damage in the back.
The treatment options for back pain
The treatment options for back pain vary depending on the cause and severity of the pain. Some common treatments include:
Over-the-counter pain medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve mild to moderate back pain.
Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises and stretches to strengthen your back muscles and improve flexibility.
Acupuncture: This alternative treatment involves inserting thin needles into specific points in the body to relieve back pain.
Hot/Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and temporarily relieve pain.
Chiropractic Care: A chiropractor uses hands-on manipulation techniques to realign the spine and alleviate back pain.
Injections: If other treatments do not provide relief, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain in the back.
Spinal Manipulation: Chiropractors or osteopathic doctors use hands-on techniques to manipulate the spine and relieve back pain.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be recommended to treat underlying conditions causing back pain, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Conclusion
Back pain is a common problem that can significantly impact your daily life. While certain risk factors, such as age and heredity, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to prevent and manage back pain. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, staying active, and managing stress are all essential for keeping your back strong and healthy. If you experience persistent or severe back pain, it is crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. You can lead a pain-free life with a healthy back by making small lifestyle changes and seeking timely medical help when needed. So always prioritize taking care of your back to maintain your overall health and well-being.
With this comprehensive guide on back pain causes, prevention tips, and treatment options, you can take charge of your back health and prevent the discomfort associated with back pain. Always listen to your body and seek professional help for a healthy, pain-free back. So, implement these practical tips today to keep your back strong and pain-free for years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause back pain?
Yes, stress can lead to muscle tension in the back, resulting in pain and discomfort. Practicing stress management techniques can help reduce the risk of developing back pain.
Can a hernia cause lower back pain?
Yes, a hernia can cause lower back pain. When an abdominal hernia, such as an inguinal or umbilical hernia, protrudes, it can press on nearby nerves, leading to pain that radiates to the lower back. Additionally, the strain from compensating for the discomfort of a hernia can cause muscle tension and discomfort in the lower back region.
Although hernias primarily affect the abdomen, their impact on surrounding structures can contribute to lower back pain. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment if a hernia is suspected of causing lower back pain.
Does masturbation cause back pain?
There is no scientific evidence to where it suggests that masturbation causes back pain. However, certain positions or movements during sexual activity may strain the back muscles and cause temporary discomfort.
If you experience persistent back pain from any activity, it is essential to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
At what age does back pain start?
Back pain can start at any age, but it becomes more common as you get older due to changes in the spine and muscles. It is estimated that around 80% of adults will experience back pain at some point. However, practicing good posture, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce your risk of developing back pain as you age.
Always prioritize taking care of your back to support overall health and well-being. So, regardless of age, incorporate these preventative measures into your daily routine for a solid and healthy back. Monitor your habits and seek timely medical help for long-term relief from back pain.
Does high blood pressure cause back pain?
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common condition that can have various health implications, but it is not typically a direct cause of back pain. However, there are several indirect ways in which high blood pressure might be associated with back pain:
1.Kidney Issues: Hypertension can lead to kidney damage over time. Since the kidneys are located in the lower back area, kidney problems can manifest as lower back pain.
2.Medication Side Effects: Some medications used to treat high blood pressure can have side effects, including muscle pain or discomfort, which might be perceived as back pain.
3.Vascular Problems: High blood pressure can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arteries narrow and harden. Reduced blood flow due to vascular problems can cause pain in various body parts, including the back.
4.General Health Impact: High blood pressure can affect overall health and contribute to conditions such as obesity, which can put additional strain on the back muscles and spine, leading to pain.
While high blood pressure is not a direct cause of back pain, it can contribute to conditions that may lead to discomfort in the back. It’s essential to manage hypertension through lifestyle changes and medication to prevent these potential complications.
Can a mattress cause back pain?
Yes, a mattress that does not provide proper support can lead to back pain. A mattress that is too soft or firm can cause misalignment of the spine, leading to discomfort and pain in the back. Choosing a mattress that provides adequate support for your body and promotes good posture while sleeping is essential.
Regularly rotating and replacing old mattresses can help prevent back pain. Remember to consult a doctor if you experience persistent back pain even after changing your mattress for proper diagnosis and treatment. Prioritizing good sleep habits and investing in a supportive mattress can go a long way toward maintaining a healthy and pain-free back.


Trackbacks/Pingbacks